Wikipedia defines foundation as: A foundation (or, more commonly, base) is the element of an architectural structure which connects it to the ground, and transfers loads from the structure to the ground. Foundations are generally considered either shallow or deep.
It is advisable to know suitability of each types of foundation before deciding which best suit your design type and soil. We would discuss them briefly below:
Types of Foundation and their Uses
The following are different types of foundations used in construction:
1. Shallow foundation
* Strip foundation
* Pad or Individual footing foundation
* Raft or Mat foundation
2. Deep Foundation
* Pile foundation
We would only focus on the shallow foundation in our discussion here;
1a. Strip foundation
Strip footings are commonly found in load-bearing masonry construction, and act as a long strip that supports the weight of an entire wall. These are used where the building loads are carried by entire walls rather than isolated columns.
This type of foundations are used on good firm soils – and majorly for bungalows because the walls of this type of building are all load bearing walls (i.e transmitting load from the roof, down to the foundation).

Looking at the pictures above, you would notice the ground in question is a either rocky or clayey, coupled with the fact we’re building a bungalow.
Recommendation: If you have a strong, clay or rocky soil and you’re building a residential bungalow on it – then the best foundation to use is a Strip Foundation, the rule however changes if you’re building a warehouse (double volume) because there are less load bearing walls to support the roof above – this this case, the pad foundation (discussed below is the right foundation to use)

Note: Strip foundation could be reinforced or plain (without reinforcement)
1b. Pad foundation
Pad foundations are used to support an individual point load such as that due to a structural column. This type of foundation has more to do with the type of structure rather than the type of soil. It could be used on both strong and weak soil, however unlike on strong soil, its use on weak soil requires stabilizing the soil before considering pad foundation.
Pad foundations are used for structures that transmit load to the foundation via columns – and are used for warehouses, workshops, and framed structures (in this cases, the block-walls are NOT load bearing) all load are transmitted through columns or a combination of columns and beams.
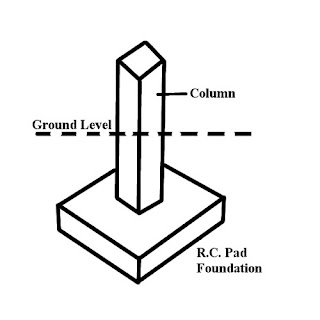
Recommendation: If you’re building a warehouse, workshop or structures that have limited of no wall partition, then this is the foundation to use – It can be used on strong and weak soil. One weak soil, the soil has to be stabilized and left to settle / rammed mechanically before the pad can be used. The size of the pad foundation and columns are determined by
In good soil areas and for storey buildings, a combination of strip and pad foundation can be used to reduce cost, or pad foundation could be used (solely) where the storey building is a frame structure.
The columns on pad foundation could be made of concrete or structural steel (below pics shows a structural steel on pad foundation)


1c. Raft foundation
A raft foundation is a reinforced concrete slab under the whole of a building. i.e ‘floating’ on the ground as a raft floats on water. Raft foundation are used on swampy, waterlogged or sandy (collapsible) soil. This type of foundation spreads the load from a structure over a large area.

It is also used for basement floors even in strong soil with a retaining (concrete) wall around it.
Recommendation: If you’re building a bungalow, 1 storey or 2 storey structure on a weak soil, then raft foundation is the foundation to use. They are generally constructed on a compacted (hardcore) base for best results and a layer of 50mm weak concrete (blinding) laid to allow a level surface for forming of the raft.


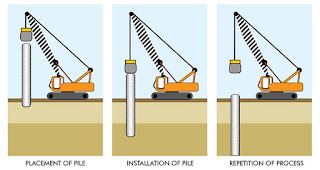
2. Pile foundation
Pile foundations are principally used to transfer the loads from superstructures, through weak, compressible strata or water onto stronger, more compact, less compressible and stiffer soil or rock at depth.

In whatever type of foundation used, waterproofing membrane should be considered.
Disclaimer: Pictures used for this reports are random pictures gotten from the internet, we do not claim ownership.
Thanks….




Share your thoughts